Septoplasty
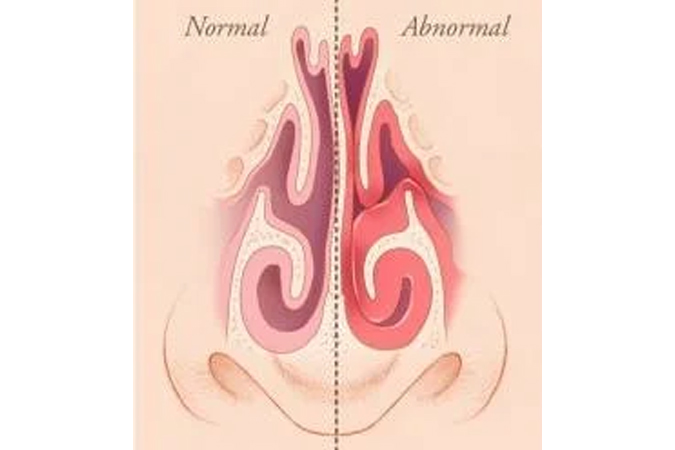
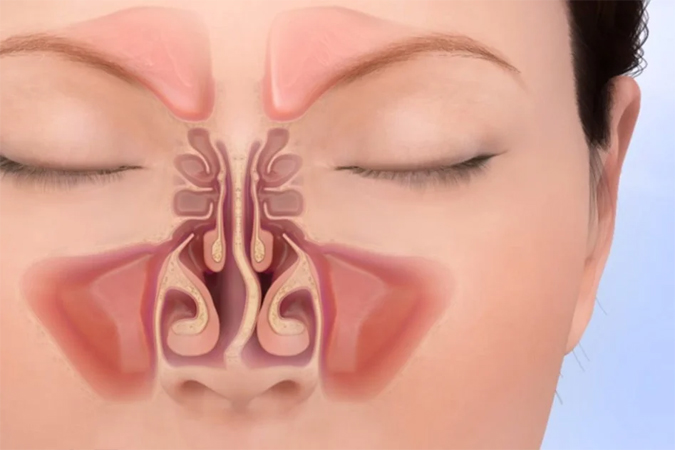
Septoplasty is a surgical procedure performed to correct a deviated septum. The septum is the cartilage and bone that divides the nasal cavity into two separate chambers. When the septum is deviated, it can obstruct airflow through one or both sides of the nose, leading to symptoms such as nasal congestion, difficulty breathing, and recurrent sinus infections.
During septoplasty, the surgeon makes incisions inside the nose and carefully repositions or removes portions of the deviated septum to straighten it and improve airflow. This procedure is typically performed under general anesthesia and can often be done on an outpatient basis, meaning the patient can go home the same day.
Septoplasty can provide significant relief from nasal congestion and breathing difficulties, as well as reduce the frequency of sinus infections. Recovery from septoplasty usually involves some discomfort, swelling, and nasal congestion for a few days to a week, but most patients experience improvement in their symptoms within a few weeks after surgery.